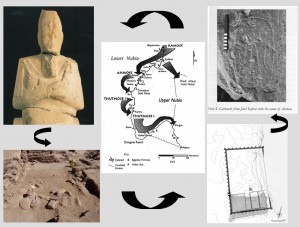
A remarkable object, SAV 002, of possible 19th Dynasty date from Sai Island was already discussed in this blog – it seems to present some kind of door sealing with a cartouche stamp of [Men]-maat-Ra (Seti I), finding close parallels at Amara West.
In a paper just published in Egitto et Vincino Oriente 37, 2014 (Budka 2015), I stated in relation to this piece: “Future fieldwork might allow a better understanding of the relations between Sai and Amara West in the early Ramesside period – SAV 002 and its parallels from Amara West can be regarded as important hints for contemporaneous administrative activities at both sites.”
Writing this back in summer 2014, I was of course not expecting to see this hope for further evidence coming true already in the very next season!
Although we are far away from understanding the complete picture, the 2015 field season provided multiple proof for the presence of early Ramesside officials and corresponding activities on Sai:
1) At SAV1 West, a back-filling in the Northeastern corner of Square 1 could be dated to the early 19th Dynasty. It covers the remains of a small oven room where several phases of use were documented. Obviously the room was built during the mid-18th Dynasty and in use until the late 18th Dynasty – the Ramesside material implies a possible abandonment of the structure.
2) Scattered ceramics datable to the Ramesside period were also found at SAV1 East – in disturbed contexts above Building A.
3) Finally, SAC5 has yielded both worked stones and ceramics datable to the 19th Dynasty. Two new inscribed monuments of the jdnw n Kush Hornakht are especially relevant – this high official was active during the reign of Ramesses II, well attested by monuments found especially in Abri and Sai.
The new finds allow us to tentatively assume that the stela set up by Seti I on Sai which was discovered during the early French excavations (Vercoutter 1972; el-Saady 2011), is much more than random evidence, but actually reflects the ongoing importance of Sai as (some kind of) Egyptian administrative centre. Field research in both Sai and Amara West will continue to provide more and more pieces to reconstruct this complex puzzle.
REFERENCE
Budka 2015 = J. Budka, The New Kingdom in Nubia: New results from current excavations on Sai Island, Egitto e Vicino Oriente 37, 2014 [2015], 55-87.
el-Saady 2011 = H. el-Saady, Egypt in Nubia during the Reign of Seti I, in M. Collier, S. Snape (ed.), Ramesside Studies in Honour of K.A. Kitchen, Bolton 2011, 433-437.
Vercoutter 1972 = J. Vercoutter, Une campagne militaire de Séti en Haute Nubie. Stèle de Saï S. 579, «Revue d’Égyptologie» 24, 1972, 201-208.