In the last months, a total number of 492 faunal remains were identified and analyzed from the New Kingdom town of Sai Island. The identification and analysis of species was carried out on Sai Island during the field season 2014 and it was continued in Vienna (Austria) at the Museum of Natural History (1st Zoological Department, Archaeozoology) and at the Department of Palaeontology (University of Vienna). My sincere thanks go therefore to the Sudanese Authorities (NCAM and especially our inspector Huda Magzoub) and also to Dr. Erich Pucher and Dr. Karl Kunst for their constant support here in Vienna!
The bone deposits derive from SAV1 North within the New Kingdom town of Sai, from three levels numbered from 5 to 3, datable to the 18th Dynasty (see Budka and Doyen 2013). Human intervention related to butchery techniques has been detected on the faunal remains from all levels investigated.
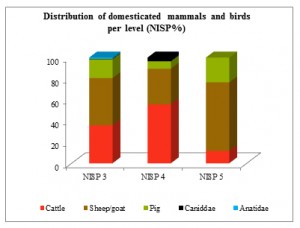
Diagram 1: Distribution of mammals and birds from Sai Island, SAV1 North according to the Number of Identified Specimens (NISP) for levels 3-5. The prevalent species are mainly sheep/goats and cattle, but with some differences from level 5 to 3.
The faunal composition demonstrates the prevalence of domesticated mammal species at SAV1 North (Diagram 1). However, the very limited number of bones available from good archaeological contexts (levels 5-3) has to be stressed ‒ the material did not allow statistical processing and all results are of a tentative character based on a restricted corpus of faunal remains. Yet, I do believe that there is rich potential in the study of the animal bones from the New Kingdom town area of Sai, especially with the new stratified material from recent excavations as in SAV1 West, still waiting for analysis. Today, I would like to present some first data concerning one of the interesting species among the attested mammals: the pig (Sus scrofa f. domestica).
Pigs are recorded at a relatively higher percentage, after sheep/goat, at level 5, but a reduction follows at level 4. The profile changes at level 3, where the number of the bones is again increasing.
Pigs correspond to 8 bones from level 5, 10 from level 4 and 55 from level 3. As it is illustrated in Diagram 1, they are found at a relatively high percentage at level 5. Evidence from level 4 demonstrates that cattle and caprine prevail, whereas pigs are found in a smaller number. Pigs remain just the third prevalent species at level 3, although the total number of bones is higher.
For level 5 and the small number of bones, the skeletal part distribution is not well understood. A small amount of vertebrae, humerus and dentes are noted for this level. Dentes, tarsals and pelvis have mainly survived from level 4. More remains have been recovered from level 3. Mandibles prevail (14.5%) followed by humerus (10.9%), costae (9%), radius (7.2%) and pelvis (7.2%). Smaller bones (carpals, tarsals, and phalanges) lack completely.
The analysis of the age profile shows that the vast majority of the material coming from level 3 belongs to individuals between 1 and 2.5 years. Some of them are younger than 1 year and only in one case up to 3.5 years. The dental examination confirms the young age for the majority of the animals (16 months). Level 4 presents mainly individuals younger than 2-3 years and in one case older than 3.5 years. From level 5 only one individual is recorded, which seem to be younger than 1 year.
The butchery marks recorded on pigs are mainly related to disarticulation and portioning.

Mandibula of a pig from Level 4.

Proximal part of a humerus from Level 4.
To conclude, pigs recovered at SAV1 North were slaughtered at the optimum age for meat consumption. The very rare cases of older pigs could be related with the needs of reproduction. It is noteworthy that as far as we know pigs in Nubia are mainly connected with Egyptian presence. For instance, the pyramid tomb G301 at Cemetery D of Amara West (19th Dynasty) brought to light a neonate piglet from the western chamber (Binder et al. 2011, 53). On the other hand, pigs have not been found at Kerma in the town or cemeteries (see the studies by L. Chaix, e.g. 1988 and the extensive list of publications available at http://kerma.ch/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=40&Itemid=79#animal).
In New Kingdom Egypt, pig is among the most numerous species killed for meat and a preference for young animals is traceable in settlements (see e.g. at Amarna, Kemp 2012, 219-220).
It can be very tentatively suggested that the presence of pigs in the earliest level 5 at SAV1 North corresponds to the analysis of the ceramics from the same contexts: The material is New Kingdom in date and Egyptian in character, supporting the assessment that a Pharaonic settlement was founded on the island very early in the 18th Dynasty (cf. Budka 2011; Budka and Doyen 2013).
For now, only some preliminary tendencies for the faunal material from the New Kingdom town of Sai have been outlined. The low amount of the material studied so far has to be taken in consideration, implying that the results might significantly change during the next campaigns. However, the case study of the pig remains from SAV1 North illustrates that the study of the faunal remains from Sai will significantly contribute to the interpretation of the character of the site during the 18th Dynasty.
References:
Binder et al. 2011 = M. Binder, N. Spencer & M. Millet, Cemetery D at Amara West: the Ramesside period and its aftermath, British Museum Studies in Ancient Egypt and Sudan 16, 2011, 47–99.
Budka 2011 = J. Budka, The early New Kingdom at Sai Island: Preliminary results based on the pottery analysis (4th Season 2010), Sudan & Nubia 15, 23–33.
Budka and Doyen 2013 = J. Budka & F. Doyen, Living in New Kingdom towns in Upper Nubia – New evidence from recent excavations on Sai Island, Ägypten & Levante 22/23, 2012/2013, 167–208.
Chaix 1988 = L. Chaix, Cinquième note sur la faune de Kerma (Soudan). Campagnes 1987 et 1988. In C. Bonnet et al., Les fouilles archéologiques de Kerma (Soudan), Genava, n.s. 36, 1988, 27–29. http://kerma.ch/index.php?option=com_wrapper&Itemid=247
Kemp 2012 = B. Kemp, The City of Akhenaten and Nefertiti. Amarna and its people, Cairo 2012.
 When scrutinised more carefully with Professor Klemm’s long experience of Pharaonic sandstone quarries, analogous chisel marks have now been identified on the sandstone outcrops of the quarries and on the blocks of stones used in the temple. Here, we would like to thank Martin Fera for lending us his geological hammer, about which we would ALL somehow manage to forget from time to time, thus creating much commotion, laughter and fun amidst our fieldwork.
When scrutinised more carefully with Professor Klemm’s long experience of Pharaonic sandstone quarries, analogous chisel marks have now been identified on the sandstone outcrops of the quarries and on the blocks of stones used in the temple. Here, we would like to thank Martin Fera for lending us his geological hammer, about which we would ALL somehow manage to forget from time to time, thus creating much commotion, laughter and fun amidst our fieldwork. This year’s survey also produced further suggestion about the Pharaonic harbour or landing ground in the adjacent alluvial platform when rock-cut features for tying ship ropes were found at least at two places. In addition, rock cut steps bearing chisel marks identical to those of the temple have also been identified.
This year’s survey also produced further suggestion about the Pharaonic harbour or landing ground in the adjacent alluvial platform when rock-cut features for tying ship ropes were found at least at two places. In addition, rock cut steps bearing chisel marks identical to those of the temple have also been identified. A thorough landscape survey has also been undertaken to understand the nature of the deposits, especially towards the northern part of the island. This has enabled us to collect data to develop a surface map of the vicinity of the town. Along with the data from the hand auger profiles, exposed sections, soil micromorphology and the surface map, a better understanding of the site setting and geomorphology of the location can be integrated within the GIS for various purposes.
A thorough landscape survey has also been undertaken to understand the nature of the deposits, especially towards the northern part of the island. This has enabled us to collect data to develop a surface map of the vicinity of the town. Along with the data from the hand auger profiles, exposed sections, soil micromorphology and the surface map, a better understanding of the site setting and geomorphology of the location can be integrated within the GIS for various purposes.