I arrived to the city of Vienna (my big dream) in the morning of August 28. Julia Budka kindly picked me up from the airport on arrival at 10:30 AM. We then went to my accommodation: Hotel Post, just around the corner of the Austrian Academy. My hotel room reminded me of the one I had during my stay in London, on the occasion of the International Training Programme at the British Museum.
I have heard about Vienna, I saw it in pictures, but I did not expect this beauty, cleanliness and high degree of organization everywhere! I really consider myself fortunate to have visited this wonderful city.
My stay in Vienna was scheduled for four days and the main task was a workshop on pottery. I was aiming for additional training in the study of Egyptian pottery thanks to the joint venture of Dr. Julia, her project and the Sudan National Museum. Back home, I am currently working on a catalogue of New Kingdom pottery in the Sudan National Museum.
On the first day, we met for lunch and had a nice tour through the city – together with the team members of AcrossBorders, some of who I know very well from Sai Island, others I just met in Vienna.
The 29th of August 2014 was a very full day for me and started at 9:30 am. We met in the office of the department Egypt and the Levant of OREA with the staff of AcrossBorders and a student interested in pottery and archaeology. Julia Budka, the director of the project and of excavations in the Pharaonic town of Sai Island, started the workshop with a presentation discussing and reviewing the last two field seasons. We spoke about dating, the settlement remains and objects.
Afterwards Giulia D’Ercole explained some of her work about the scientific analysis of the fabric from the New Kingdom town, giving some details about Nubian pottery.
Later we all went to have lunch at a famous falafel restaurant close by. In the afternoon, we started the workshop with discussing and practicing how to use the fire dogs! It was unfortunate that Nicole, the student working on the fire dogs and who I know from Sai, could not come on this occasion!
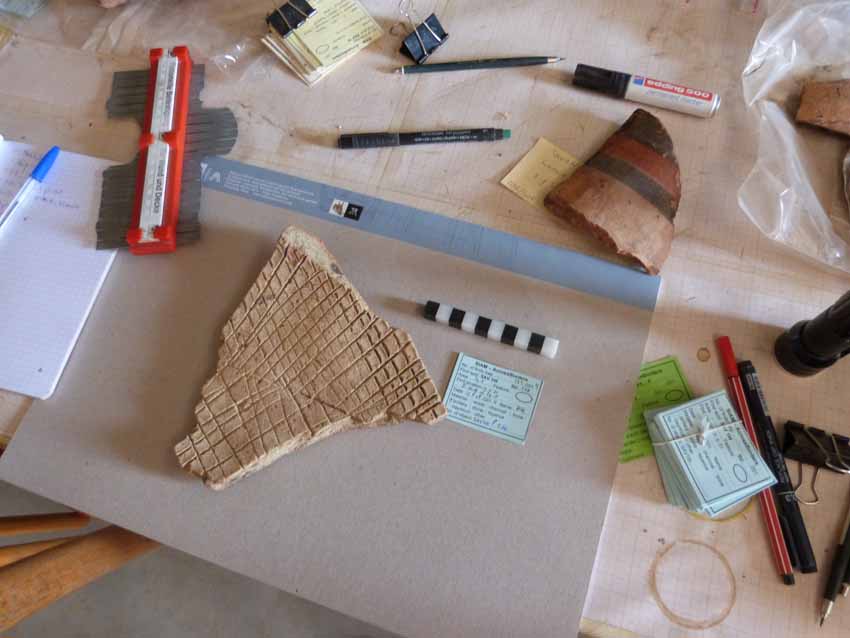
After that the workshop focused on the drawing and classification of New Kingdom pottery. Arvi Korhonen explained to the students and then they practiced with some sherds. Julia and me had now time to discuss details about the Sudan National Museum New Kingdom Pottery project: some of the vessels find very nice parallels at other sites, also at Sai. Others were familiar to Julia thanks to her experience from Egypt, especially on Elephantine.
After that I went back to the hotel where I took a little bit of rest, and then I met the group again for dinner at a restaurant just next to the oldest church of Vienna! Here I had the first original Wiener Schnitzel of my life!
This trip was a great pleasure for me – I was accompanied by Julia and her group, we saw historical monuments and also some roman archaeological remains in the heart of Vienna. What triggered my surprise was the nature of the range of architecture and I was very impressed by the architecture of the churches, ranging back to very early times.
Most enjoyable of my trip to Vienna was my visit to the amusement park Vienna, the PRATER. Here one of my escorts was Kara, Julia’s dog, who joined us at the Riesenrad and apparently enjoyed the ride as well!
On this day I tried another local speciality: a so-called Langos – a kind of a very large, fried pancake with a pleasant taste. There are similar ones in my country, but the size is much smaller and we eat it with sugar instead of with salt and garlic like the Austrians!
 After the weekend, I travelled with Julia and Jördes via Zurich airport by train to Neuchatel to attend the Conference for Nubian Studies.
After the weekend, I travelled with Julia and Jördes via Zurich airport by train to Neuchatel to attend the Conference for Nubian Studies.
Thanks to the company and programme, my visit to Austria was the most beautiful and the greatest trip to an European country in my life! Many thanks to Julia and all my colleagues in Vienna!
Last but not least, I had the great pleasure to get to know Ishraga MUSTAFA HAMID: scientist, author, poet and more from Sudan living in Vienna since 1993! We spent some wonderful time together, including a trip to the castle of Schönbrunn. Alf shokron und vielen Dank!