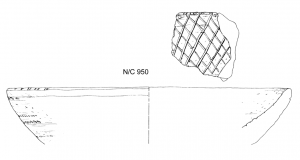
A peculiar type of vessel is frequently found in Egyptian settlements, already from the 13th Dynasty onwards (see Bader 2001, 81–83; Aston and Bader 2009). These quite large, thick walled oval, handmade trays show incised decoration on the interior – commonly depicting fishes, lotus flowers and geometric motives (see, e.g., a nice dish from Kahun, now at the Manchester Museum).
Consequently a label as “fish dish” was proposed for these trays which somehow resemble the well-known Nun-bowls of the New Kingdom (cf. Bader 2001, 81–83). However, in settlement contexts of the later Second Intermediate Period and the early New Kingdom the pattern of these trays are mostly geometrical – diagonal lines, net pattern and fish bone pattern. The function is therefore still debated – such dishes might have been used for peeling corn or scaling fishes (“Schälbecken”), as bread trays or as trays with a (still unclear) ritual function (cf. Seiler 2005, 120–121).
At all sites investigated within the framework of AcrossBorders (Sai Island, Elephantine and South-Abydos), so-called “bread trays” are well attested.
At Sai Island, the trays occur both in Egyptian Marl clay (Marl B and Marl E, a special variant of Marl B, see Arnold and Bourriau 1993, 182 and fig. 26) and in local Nile clay variants; the shapes and decoration patterns are in both cases the same. Parallels for the Marl clay examples are known, apart from Elephantine and South Abydos, from early 18th Dynasty contexts at Deir el-Ballas (Bourriau 1990, 21–22) and also from Lower and Upper Nubia (e.g. Buhen (Emery, Smith and Millard 1979, pl. 73) and Sesebi (Spence and Rose et al. 2011, 37)). As yet, the only published parallel for a Nile clay tray comes from a funerary context at Thebes (Seiler 2005, 104-5, fig. 52). However, in the Egyptian settlement at Elephantine, Nile clay trays were found in strata of the 18th Dynasty, closely resembling the ones from Sai.
Today, I searched both the Sai Island and the Elephantine New Kingdom databases for “bread trays”. The results are quite remarkable – in both cases 16 pieces for levels ranging in date from the early 18th Dynasty to the mid/late 18th Dynasty have been studied in detail and are included in the databases. At Elephantine, only four examples are made in coarse Nile clay (25 %), whereas the others are made in Marl B respectively Marl E (75 %). At SAV1North, nine examples are of a local, very coarse Nile clay (56 %) and seven have been produced in Egypt, made in a Marl B/E variant (44 %).
Of course the number of these vessels documented in detail is very small – I will have to address the same question to the general statistics of all New Kingdom contexts at SAV1North and Elephantine, not just to the database entries only. Nevertheless, I think this small, but significant difference allows already some preliminary thoughts: Maybe it was more difficult at Sai in Upper Nubia to get replacements for the “real” Marl B/E trays – thus, they were produced in local material. Alternatively one also might speculate, considering the still unknown function of the vessels, that the shape was for some reasons more popular in Sai and more frequently created on demand. It seems as if the difference in material did not make a difference for the ancient users of the trays – and this, from my perspective, makes a use as “Schälbecken” quite unlikely; the Nile clay versions are much softer and porous, not well suited for peeling organic materials. All in all, these vessels might have been fashionable in Upper Nubia because they reflected “Egyptian” life style and were foreign to the local Nubian culture – their specific outer appearance and properties which we as archaeologists use to create classifications and typologies maybe had little significance within the antique context.
References:
Arnold and Bourriau 1993 = Dorothea Arnold and Janine Bourriau (eds.), An Introduction to Ancient Egyptian Pottery, SDAIK 17, Mainz am Rhein 1993.
Aston and Bader 2009 = David A. Aston and Bettina Bader, with a contribution by Karl G. Kunst, Fishes, ringstand, nudes and hippos – a preliminary report on the Hyksos palace pit complex L81, E & L 19, 2009, 19–89.
Bader 2001 = Bettina Bader Tell el-Daba XIII, Typologie und Chronologie der Mergel C-Ton Keramik des Mittleren Reiches und der Zweiten Zwischenzeit, UZK 19, Vienna 2001.
Bourriau 1990 = Janine Bourriau, The Pottery, 15–22 and 54–65 [figs.], in: P. Lacovara, Deir el-Ballas, Preliminary Report on the Deir el-Ballas Expedition, 1980-1986, ARCE Reports 12, Winona Lake, Indiana.
Emery, Smith and Millard 1979 = Walter B. Emery, Harry S. Smith and Ann Millard, The Fortress of Buhen. The archaeological report, EEF Excavation Memoir 49, London 1979.
Seiler 2005 = Anne Seiler, Tradition & Wandel. Die Keramik als Spiegel der Kulturentwicklung in der Zweiten Zwischenzeit, SDAIK 32, Mainz am Rhein 2005.
Spence and Rose et al. 2011 = Kate Spence and Pamela Rose et al., Sesebi 2011, Sudan & Nubia 15, 2011, 34–38.