Post-excavation work is keeping us very busy at the moment in Munich, the summer term has also started with teaching and exams. Among the priorities of current tasks is the digitalization of pottery drawings in order to prepare publication-ready illustrations. These days, it was the turn of a very thought-provoking group of vessels: Egyptian cooking pots. One of these vessels is of particular interest.
A large fragment of a cooking pot from Square 4B was among my favourite finds from SAV1 East during the 2016 field season. The vessel, SAV1E P179, found still filled with ashy deposits, was sitting next to the remaining parts of a mud brick wall.
 Close by, another highlight, SAV1E 1595, a small steatite scarab, was discovered. Both finds, the cooking pot and the scarab, are coming from a room to the west of Building A – traces of pavements and various deposits allow reconstructing several phases of use in the early/mid-18th Dynasty.
Close by, another highlight, SAV1E 1595, a small steatite scarab, was discovered. Both finds, the cooking pot and the scarab, are coming from a room to the west of Building A – traces of pavements and various deposits allow reconstructing several phases of use in the early/mid-18th Dynasty.
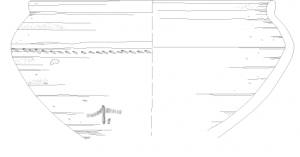
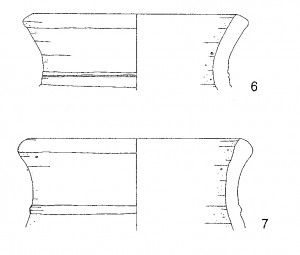
Coming back to the cooking pot SAV1E P179: After documenting the vessel in its original find position, we removed it and the content was sieved for further analyses. The cooking pot itself was put on the “priority list” for drawing – Daniela did a great job in Sai, and now in the office with our interactive multi-touch pen display.
SAV1E P179 gives really significant evidence: stratigraphically datable to the Thutmoside period, it finds close parallels at Elephantine in Upper Egypt. It is a typical example of a wheel-made, authentic Egyptian cooking pot. It was made in a very sandy Nile clay variant which was presumably produced at Elephantine/in the Aswan region – this cooking pot was therefore shipped from Egypt to Sai!
Whereas storage vessels and amphorae are commonly transported along the Nile, it is quite remarkable that also cooking pots were transported for long distances to places outside of Egypt. Imported cooking pots allowed Egyptian-style cooking in Sai during the early to mid-18th Dynasty. Obviously authentic cooking pots were considered to be important like SAV1E P179 illustrates. Our ongoing processing of the data suggests that this gradually changed in the course of the 18th Dynasty – the degree of dependence of Sai from Egypt became different and the local production of wheel-made pottery was introduced/increased.
The pottery from Sai Island New Kingdom town promises fascinating insights into the complex and developing microcosm of the site attesting to a co-existence of Egyptian and Nubian elements – we will work hard to decipher as much as possible in the next months.