During our 2014 field season on Sai Island, working in the New Kingdom town, we also devoted some time to re-organize the finds from the early French exploration of the town under Jean Vercoutter, now stored in the magazine of the French digging house. There are beautiful and important highlights among them complementing our recent findings at SAV1 East and SAV1 West.
It was a very nice coincidence that while I was just working on one particular puzzling piece we received a visit by the Amara West team directed by Neal Spencer (British Museum). I was keen on showing them this object as it seemed to have links to Amara West and the founder of this temple town, Seti I – and it came even better: they had just found something very similar during the current fieldwork!
Chiara Salvador wrote a very interesting post about the Amara object with several pictures.

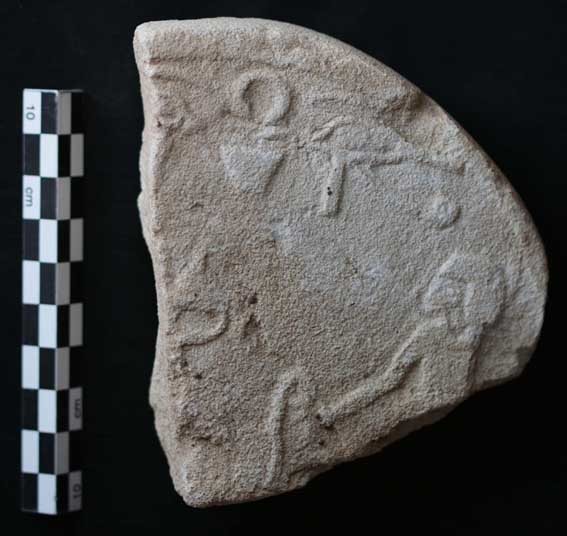
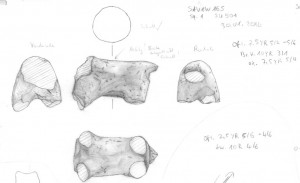
The piece of mud with impressions of cartouche shaped stamps from SAF5.
The Sai object nicely compares to the one from Amara West – unfortunately both are fragmented and parts are missing, leaving some room for doubts and discussion. It is a piece of mud with an almost triangular section, two flat surfaces at the back and a front side showing impressions of large cartouche shaped stamps. According to the French digging diary it was found together with a second fragment on December 16 1973 in the Northwestern corner of a structure labelled SAF5 in the southern part of the Pharaonic town. Unfortunately further information about the find context is not available.

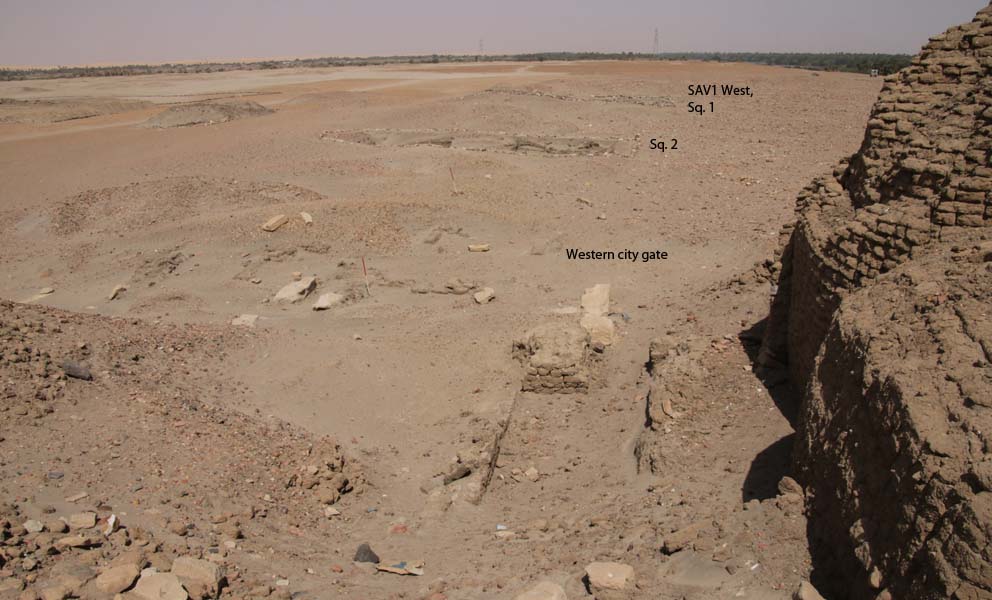
Overview of the general find spot of the mud fragment: SAF5 in the New Kingdom town.
The building complex SAF5 is still not well understood – it obviously had several building phases and its present state is very fragmented, especially on the western side, having been largely flattened during Ottoman times. Vercoutter proposed a function as door sealing for the stamped piece and this seems indeed the most likely interpretation, corresponding to what our colleagues from Amara West assume for their pieces. It is definitely not a stamped mud brick, but a flattened piece of mud with several stamp impressions on one side, one above the other (only the lower edge of the cartouche is preserved of the upper stamp) and a peculiar, almost rectangular impression on one of the back sides.
Like at Amara, the impression on SAV002 has only survived in the upper part: The sun disk (Ra) is clearly readable as well as a seated goddess Maat, with a feather on her head, holding an ankh-sign in front of her. The lower part of the cartouche stamp is missing – excactly as for the Amara West piece, it could have been Maat-[ka]-ra (Hatshepsut), [Neb]-maat-Ra (Amenhotep III) or [Men]-maat-Ra (Seti I). Hatshepsut is not yet attested on Sai Island, leaving Amenhotep III and Seti I as the more likely candidates. Amenhotep III was very active on Sai, work continued in his name at the temple for Amun-Re (Temple A), attested by inscribed blocks and other evidence. Seti I is known to have founded Amara West as administrative center of Kush, possibly shifting activities from Sai towards the new neighbouring site. Two stelae refer to military activites of the king in Nubia – one from Amara West and the other was set up in Sai where it was discovered during the early French excavations (Vercoutter 1972; el-Saady 2011)! The Abri-Delgo reach with its rich mineral resources, especially gold, was for sure of interest to Seti. The Nauri decree mentiones an as yet unidentified fortress of the king of whom building activity is also attested at Sesebi (cf. el-Saady 2011: 436). As the Sai stela indicates, it is unlikely that the island was completly abandoned during the early 19th Dynasty. At present we do have little evidence for occupation– a small number of ceramics from the town and some objects from the cemeteries date to the early 19th Dynasty, most probably to the reigns of Seti I and Ramesses II.
The relation between Sai and Amara West in the early Ramesside period are essential open questions of our current research – connecting finds from old and new excavations at both sites has much potential and promises new insights in the upcoming years!
All in all, especially considering the exciting new finds at Amara West, I do think that reconstructing the mud impression on the piece from SAF5 as Men-Maat-Ra, thus Seti I, is the most probable solution. Further interpretation and contextualizing the royal stamp from SAF5 must await future work, both in the field and the magazine, and continuous cooperation with the team currently re-excavating the Ramesside center of Kush .
References:
el-Saady 2011 = Hassan el-Saady, Egypt in Nubia during the Reign of Seti I, in: Mark Collier/Steven Snape (eds.), Ramesside Studies in Honour of K.A. Kitchen, Bolton 2011, 433-437
Vercoutter 1972 = J. Vercoutter, Une camapagne militaire de Séti en Haute Nubie. Stèle de Saï S. 579, in: RdE 24, 1972, 201-208, pl. 17.