The director of the mission thinking about the future of this area. Photo: Martin Fera.
It’s not a fairy tale, but a real-life story: telling the tale of a group of researchers, experts and trainees in the field of archaeology of different nationalities and various ages. They are Austrians, Germans, French, Belgian, Italian, Greek, British, Egyptian, Sudanese, and local Nubians, all working under the direction of someone who despite of her young age was able of leadership and brilliant management, dealing with situations severely when there was the need to.

Family, work and archaeological excavations in the Pharaonic city of Sai Island.
Photo: Martin Fera.
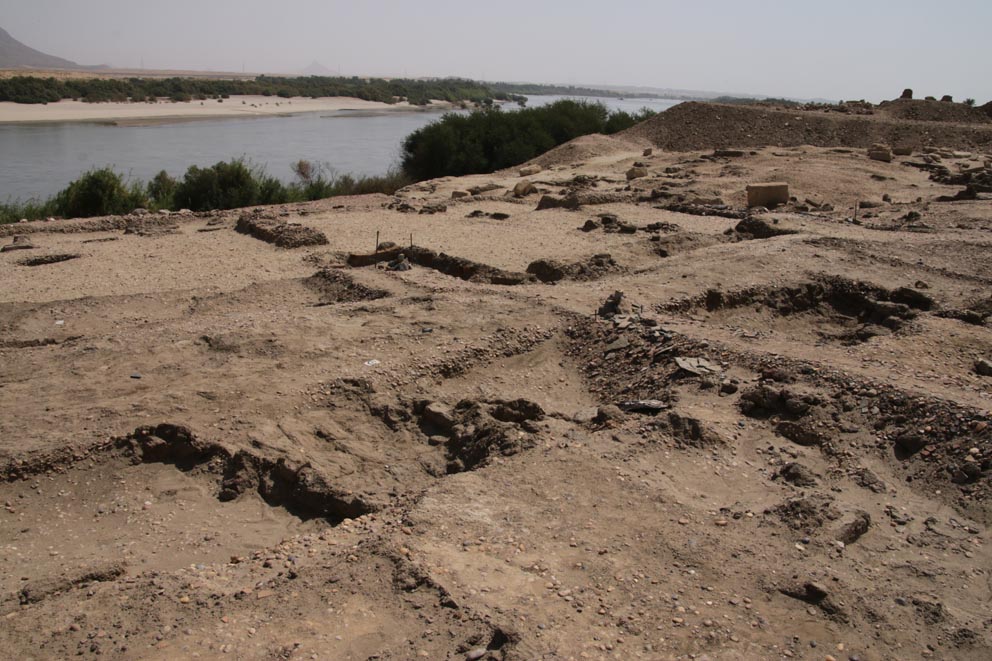
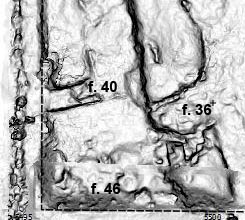
The archaeological mission covered a period of two months, during which the group of researchers was set in center of the local community in the French digging house on Sai Island. Surrounded on the east by the great Nile and a magnificent scenery with palm trees, sand and mountains. On the south, west and north of the house expand the archaeological remains of one of the greatest sites in Northern Sudan, covering a wide range of periods: This is Sai lsand, or as the locals call it, the Land of Khalil. The property of the famous Sudanese poet (Khalil Frah) , who used to live on this island, has still survived in the extreme north of the island.





 Sai Island archaeological site in the heart of beautiful landscape (Photos: Martin Fera)
Sai Island archaeological site in the heart of beautiful landscape (Photos: Martin Fera)
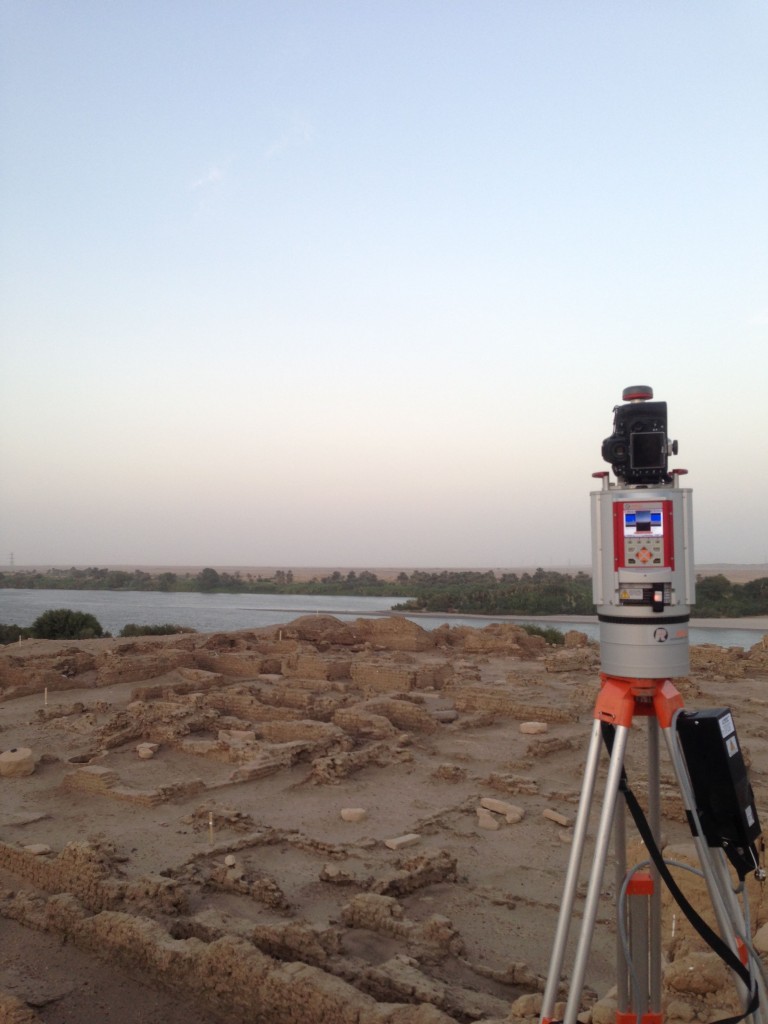
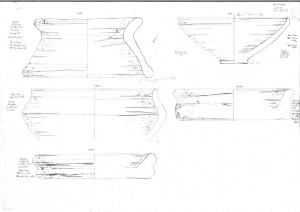
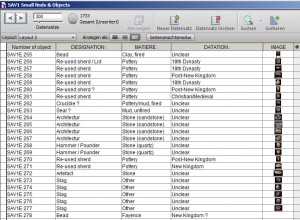
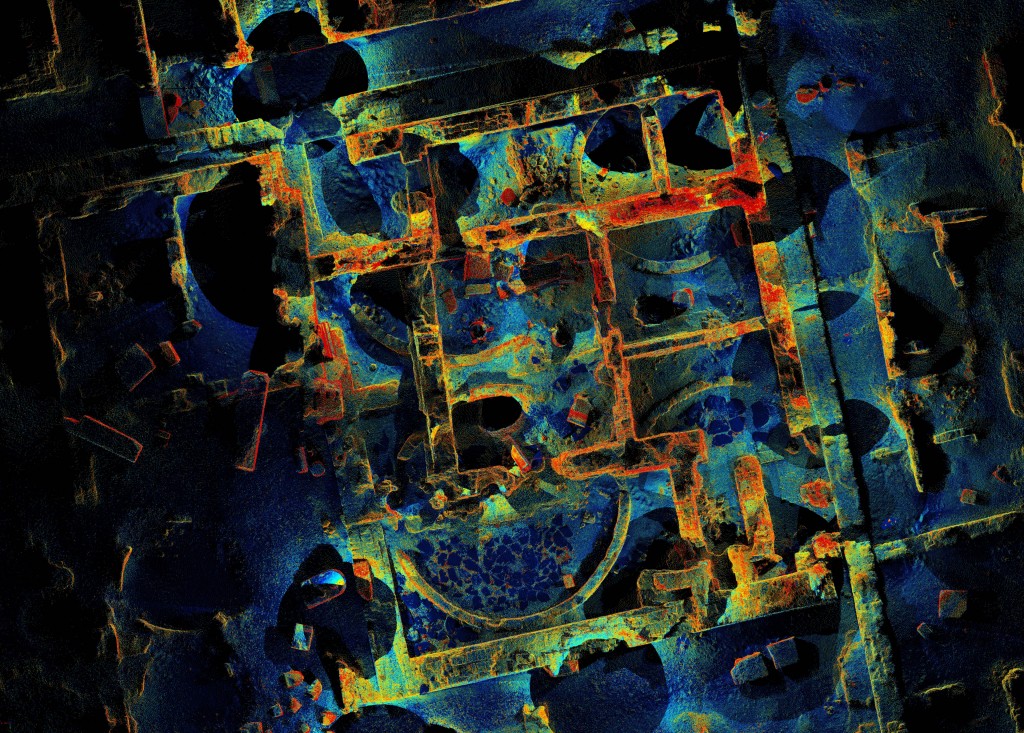
The schedule of the mission required very hard work in the field, conducting archeological excavations, and also documentation in the lab, especially with the study collection of Pharaonic Egyptian antiquities characteristic for Upper Nubia.

The field work team members during office work in the afternoon. Photos: Huda Magzoub.

The tasks of the director Julia were immense, as the administration of the house, field work and mission accumulated with her beloved study and classification of pottery.

High expertise in the classification of large amounts of pottery from the Pharaonic town of Sai Island. Photos: Huda Magzoub.

 Documentation and drawing of the ceramics were achieved with the help of a group of German, Austrian and Italian students and archaeologists. The study of pottery from the New Kingdom town of Sai, and here especially of the proportion of Nubian vessels and wares, plays a significant role in understanding 18th Dynasty Sai.
Documentation and drawing of the ceramics were achieved with the help of a group of German, Austrian and Italian students and archaeologists. The study of pottery from the New Kingdom town of Sai, and here especially of the proportion of Nubian vessels and wares, plays a significant role in understanding 18th Dynasty Sai.



Members of the pottery study group: Dr Giulia, Julia, Nicole (and Elke, not in the picture). Photos: Huda Magzoub.
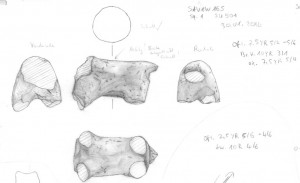
Another important aspect of understanding Sai is the study of animal bones – this year undertaken by Konstantina (Nadia) Saliari.

Study and classification of the Pharaonic animal bones from Sai. Photo: Huda Magzoub.

More specialists: Dr Erich, Dr Ingrid, Dr Robert and Florence (the last three not in the photo), had special tasks and worked in various areas. Photo: Martin Fera.
The director of the mission did not forget to reward her team for the hard work, and also tried to find ways to come together with the local community despite the tight working schedule. During the two months she organized trips to visit archaeological sites (Soleb, Sedeigna, Gebel Ducha, Sesebi and of course to Amara West in the North). In addition, interconnection and communication with the local community and families on Sai was achieved by joining them at their ceremonies, both on formal and informal occasions.

Team members of Sai Island visit other archaeological sites. Photos: M. Fera.

The reception and a number of visits by local residents, foreign missions (visit of the British Museum team working at Amara West, visit of the French ambassador and his companions) and by staff of the National Authority for Antiquities and Museums has to be mentioned.

Photo: Martin Fera.
The archaeological season on the island has ended with much joy and celebrations, wishing the advent of a new year 2015 inshaallah.