Today was the hottest day so far in the 2015 season – unfortunately not yet hot enough to prevent the numerous nimiti-flies from being very active…
This week was extremely busy and successful – in both areas (SAV1 East and SAV1 West) new mud brick walls were discovered and the number of finds and pottery increased much. Object registration continues by Kenneth Griffin and Meg Gundlach – the database comprises already 2576 objects ranging in date from the Paleolithic Period to Ottoman times. The number of items datable to the 18th Dynasty rises with every day of fieldwork.
One of the highlights among the small finds from this season is definitely an intact, small cowroid fayence amulet depicting the goddess Taweret on its flat side. It was found close to the bottom surface of the town wall’s foundation in Square 1S.
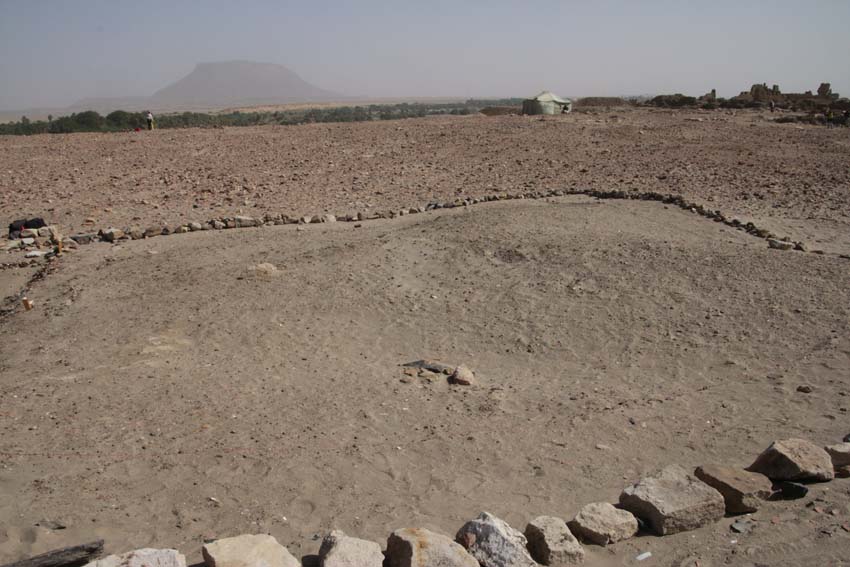
In Square 1S, Martin Fera, Stefanie Juch and their gang of workmen have exposed some fragile street deposits in the lane running along the inner side of the town enclosure as well as in situ mud brick structures in the eastern half of the square. A particularly promising structure is located in its southeastern corner – still filled with dense mud brick debris, worked stones and pottery fragments its date remains to be clarified in the upcoming week.
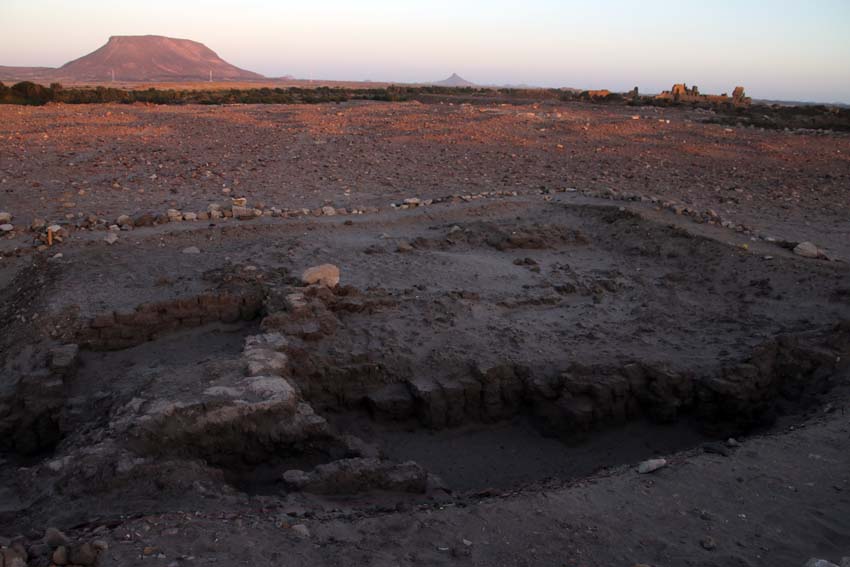
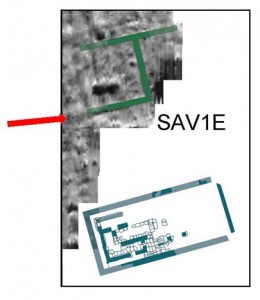
 At SAV1 East, Jördis Vieth, Huda Magzoub and their team of local workmen have exposed more remains of pavements and new sections of walls in Square 4. Due to the poor state of preservation, work here is very challenging – I am nevertheless very positive that we will be able to understand the stratigraphical relations of the scattered remains in the next weeks. The present working hypothesis is that there are early 18th Dynasty structures in the southern part of Square 4 – pre-dating Building A and finding close parallels around Temple A (excavated by Michel Azim) and in Square 2 of our excavation (storage bin feature 14).
At SAV1 East, Jördis Vieth, Huda Magzoub and their team of local workmen have exposed more remains of pavements and new sections of walls in Square 4. Due to the poor state of preservation, work here is very challenging – I am nevertheless very positive that we will be able to understand the stratigraphical relations of the scattered remains in the next weeks. The present working hypothesis is that there are early 18th Dynasty structures in the southern part of Square 4 – pre-dating Building A and finding close parallels around Temple A (excavated by Michel Azim) and in Square 2 of our excavation (storage bin feature 14).
Furthermore, Giulia D’Ercole joined us this week – she has already started to sample pottery vessels for iNAA analysis in Vienna. The focus of the 2015 season is on Egyptian style vessels – both imported ones from Egypt and locally produced wheel-made vessels.
Geoarchaeological research by Sayantani Neogi and Miranda Semple commenced this week as well – they successfully surveyed parts of the hinterland of the New Kingdom town. Miranda starts sampling archaeological deposits for micromorphological analysis at SAV1 West next week.
All in all, everything worked out according to schedule with more than satisfying results so far – and with two weeks of fieldwork in the town waiting for us!