The reuse of pottery vessels or individual sherds for various purposes is a very common phenomenon throughout the ages and cultures – evidence for material-saving recycling processes in antiquity (see Peña 2007). Re-cut pot sherds as tools with multiple functions are frequently found at New Kingdom domestic sites as can be illustrated by material from Qantir (Raedler 2007; Prell 2011, 92) and Elephantine (Kopp 2005b; see also Budka 2010c). Such a reuse of ceramics is also attested in Nubian cultures, e.g. for cosmetic palettes (Williams 1993, 45 with note 49).
It comes therefore as no surprise that the small finds of our new excavation area within the Pharaonic town of Sai Island, SAV1 East, comprise a large number of reused sherds, similar to SAV1 North. From a total of 322 registered finds from SAV1 East, 103 have been classified as reused sherds. Among these 103 pieces, 17 can be dated to the 18th Dynasty, another 3 as more general to the New Kingdom and 4 pieces are from Nubian sherds of unclear date, but with a possible origin in the New Kingdom.

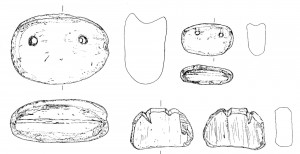
Example for reuse of lower part of dish as lid/cover
In sum, only 20% of all the reused sherds are connected with the Thutmoside activity at SAV1 East. The majority originates from the Post-New Kingdom. The objects securely dated to the 18th Dynasty include: 7 ring bases of dishes, re-cut to be used as lids or covers, 5 scrapers, 4 fragmented pieces of unclear function (most probably also used as scrapers) and 1 small disk, possibly a token.
Among the scrapers, a preference for Nile silt plates and dishes is notable; only SAV1E 290 is a reworked piece from a Marl clay vessel – this scraper was re-cut from a large storage vessel, a type known as meat jar. As yet, no fishing weights in the shape of reused sherds – commonly attested at Egyptian sites, e.g. at Elephantine – have been found at SAV1 East.

SAV1E 084: fragment of reused ringbase of 18th Dynasty dish.

SAV1E 006: fragmented re-cut sherd.
In sum, although still much smaller in number, the types and variants of reused sherds discovered in 2013 at SAV1 East parallel the findings from five years of excavation in SAV1 North. Further fieldwork will investigate whether this is accidental based on the small quantity, or whether this group of artefacts reflects similar activities in the different sectors of the Pharaonic town of Sai Island.
References:
Budka 2010 = Budka, J., Review of Die Keramik des Grabungsplatzes Q1 – Teil 2; Schaber – Marken – Scherben. Forschungen in der Ramses-Stadt, Die Grabungen des Pelizaeus-Museums Hildesheim in Qantir – Pi-Ramesse 5, ed. by E. B. Pusch & M. Bietak, Hildesheim 2007, Orientalische Literaturzeitung 105/6, 2010, 676–685.
Kopp 2005 = Kopp, P., VI. Small finds from the settlement of the 3rd and 2nd millenium BC, 17, in: D. Raue et al., Report on the 34th Season of Excavation and Restoration on the Island of Elephantine [http://www.dainst.org/sites/default/files/medien/en/daik_ele34_rep_en.pdf?ft=all]
Peña 2007 = Peña, J. T., Roman Pottery in the Archaeological Record, Cambridge 2007.
Prell 2011 = Prell, S., Einblicke in die Werkstätten der Residenz. Die Stein- und Metallwerkzeuge des Grabungsplatzes Q1, Forschungen in der Ramses-Stadt, Die Grabungen des Pelizaeus-Museums Hildesheim in Qantir – Pi-Ramesse 8, Hildesheim 2011.
Raedler 2007 = Raedler, C., Keramikschaber aus den Werkstätten der Ramses-Stadt, 1–266, in: E. B. Pusch (ed.), Die Keramik des Grabungsplatzes Q I – Teil 2. Schaber – Marken – Scherben, Forschungen in der Ramses-Stadt, Die Grabungen des Pelizaeus-Museums Hildesheim in Qantir – Pi-Ramesse 5, Hildesheim 2007.
Williams 1993 = Williams, B. B., Excavations at Serra East. A-Group, C-Group, Pan Grave, New Kingsom, and X-Group Remains from Cemeteries A-G and Rock Shelters, OINE X, Chicago 1993.