One of the main goals of AcrossBorders is to improve our understanding of the population on Sai Island during the New Kingdom and to explore the nature of the coexistence of Egyptians and Nubians. Who were the occupants of the newly founded town in the 18th Dynasty as far as their cultural identity is concerned ‒ Egyptians, Egyptianized Nubians or a mix of both?
Archaeological studies dealing with ethnicity, groups and identity have markedly increased in recent decades (cf. Brather 2004; Gramsch 2009). In Egyptian/Nubian archaeology, some studies have addressed aspects of cultural and ethnical identities (e.g. Meskell 1999; Meskell 2001; Smith 2003). The site of Tombos in Upper Nubia can be mentioned as a ready parallel for studies of biological identities of people buried there (Buzon 2006, 2008) and for a complex social diversity according to the material culture (Smith 2003). Recent studies at Amara West attempt to distinguish between Nubian and Egyptian features within the town (Spencer 2010). Ethnicity has also been addressed with regards to domestic evidence at Askut (Smith 1995).
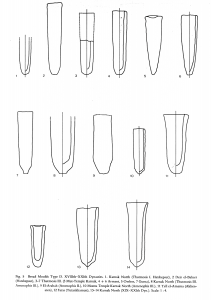
On Sai Island, the two main cemeteries of the New Kingdom are located south of the town and were labelled as SAC5 and SACP1. Future work of AcrossBorders can now rely on a substantial monograph on SAC5 recently published: Anne Minault-Gout and Florence Thill, Saï II. Le cimetière des tombes hypogées du Nouvel Empire (SAC5), FIFAO 69, Cairo 2012.  This second monograph on the work of the French Archaeological Mission on Sai Island presents in detail results of the exploration in the cemetery, which already began in the 1970s. SAC5 is of major importance as it was in use for a long period of time, covering the New Kingdom as well as the pre-Napatan period (the so called Third Intermediate Period in Egypt). Its rock-cut tombs with mostly pyramidal superstructures find close parallels in Nubia (e.g. at Soleb, Amara West and Aniba), but also in Egypt (e.g. in the Theban necropolis).
This second monograph on the work of the French Archaeological Mission on Sai Island presents in detail results of the exploration in the cemetery, which already began in the 1970s. SAC5 is of major importance as it was in use for a long period of time, covering the New Kingdom as well as the pre-Napatan period (the so called Third Intermediate Period in Egypt). Its rock-cut tombs with mostly pyramidal superstructures find close parallels in Nubia (e.g. at Soleb, Amara West and Aniba), but also in Egypt (e.g. in the Theban necropolis).
Saï II (Minault-Gout/Thill 2012) is highly recommended to all interested in New Kingdom Nubia! The volume offers detailed descriptions of 24 excavated tombs, referring to architecture, finds, ceramics and interrelationships between graves as well as to the inhabitants of Sai during the New Kingdom. The mortuary evidence from SAC5 strongly supports the findings from the New Kingdom town that there was a complex community of Egyptians and Nubians on Sai Island.
References
Brather, S. 2004: Ethnische Interpretation in der frühgeschichtlichen Archäologie: Geschichte, Grundlagen und Alternativen, Ergänzungsbände zum Reallexikon der germanischen Altertumskunde 42, Berlin.
Buzon, M. R. 2006: Biological and Ethnic Identity in New Kingdom Nubia. A Case Study from Tombos, Current Anthropology 47.4, 683–695.
Buzon, M. R. 2008: A Bioarchaeological Perspective on Egyptian Colonialism in the New Kingdom, JEA 94, 165–182.
Gramsch, A. 2009: Die Gleichzeitigkeit des Ungleichzeitigen: Überlegungen zum Kulturwandel, in A. Zeeb-Lanz (ed.), Krisen – Kulturwandel – Kontinuitäten. Zum Ende der Bandkeramik in Mitteleuropa. Beiträge der internationalen Tagung in Herxheim bei Landau (Pfalz) vom 14.–17. 06. 2007, Internationale Archäologie. Arbeitsgemeinschaft, Symposium, Tagung, Kongress 10, Rahden/Westf., 9–25.
Meskell, L. 1999: Archaeologies of Social Life. Age, Sex, Class et cetera in Ancient Egypt, Oxford.
Meskell, L. 2001: Archaeologies of Identity, in I. Hodder (ed.), Archaeological Theory Today, Cambridge, 187–213.
Minault-Gout, A./Thill, F. 2012: Saï II. Le cimetière des tombes hypogées du Nouvel Empire (SAC5), FIFAO 69, Cairo.
Smith, S. T. 1995: Askut in Nubia. The economics and ideology of Egyptian imperialism in the second millennium B.C., Studies in Egyptology, London/New York.
Smith, S. T. 2003: Wretched Kush. Ethnic identities and boundaries in Egypt’s Nubian Empire, London/New York.
Spencer, N. 2010: Nubian architecture in an Egyptian town?, Sudan & Nubia 14, 15–24.