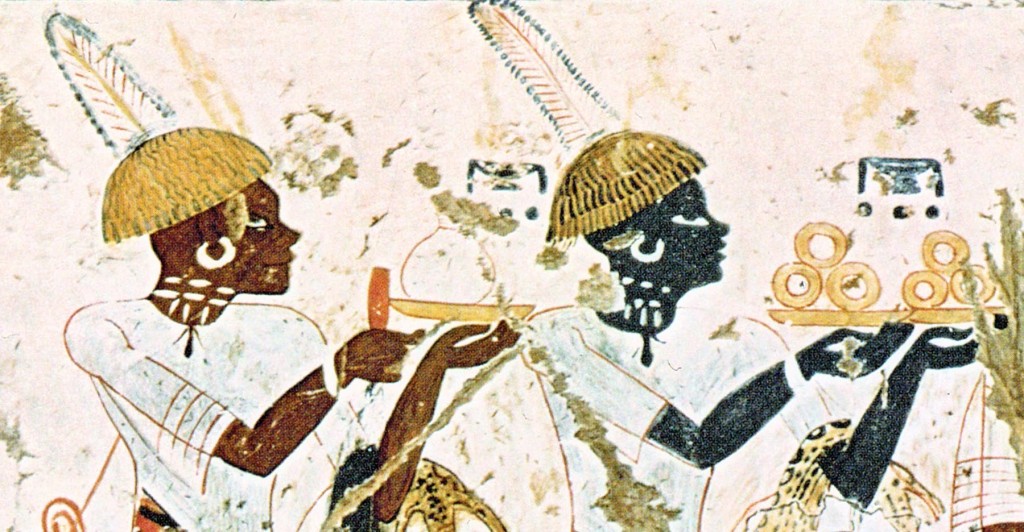
Figurative vessels from Ancient Egypt (see Bourriau 1987) include feminoform vessels with modelled breasts and often plastic arms. Such jars are attested in a variety of forms (see especially Seiler 2006 for the distinction between “Hathor” and “Isis” vases) and derive primarily from tombs (cf., e.g., Lopez Grande/de Gregorio 2009). In recent years, feminoform vessels have also been recorded from domestic contexts at settlements like Elephantine, the town area of Abydos and also Sai Island (Budka forthc.).
Although more common in the New Kingdom, pottery vessels with applied breasts and feminine faces are already known from the Middle Kingdom onwards (Stevens 2006: 171 with literature). They have often been labelled as “milk vessels”; various authors associate them with the cult of Hathor (e.g. Bourriau 1982: 78; Hope 1982: 87; Smith 2003: 47).
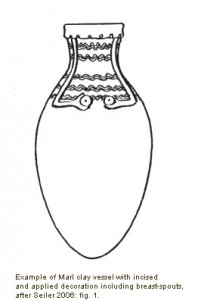
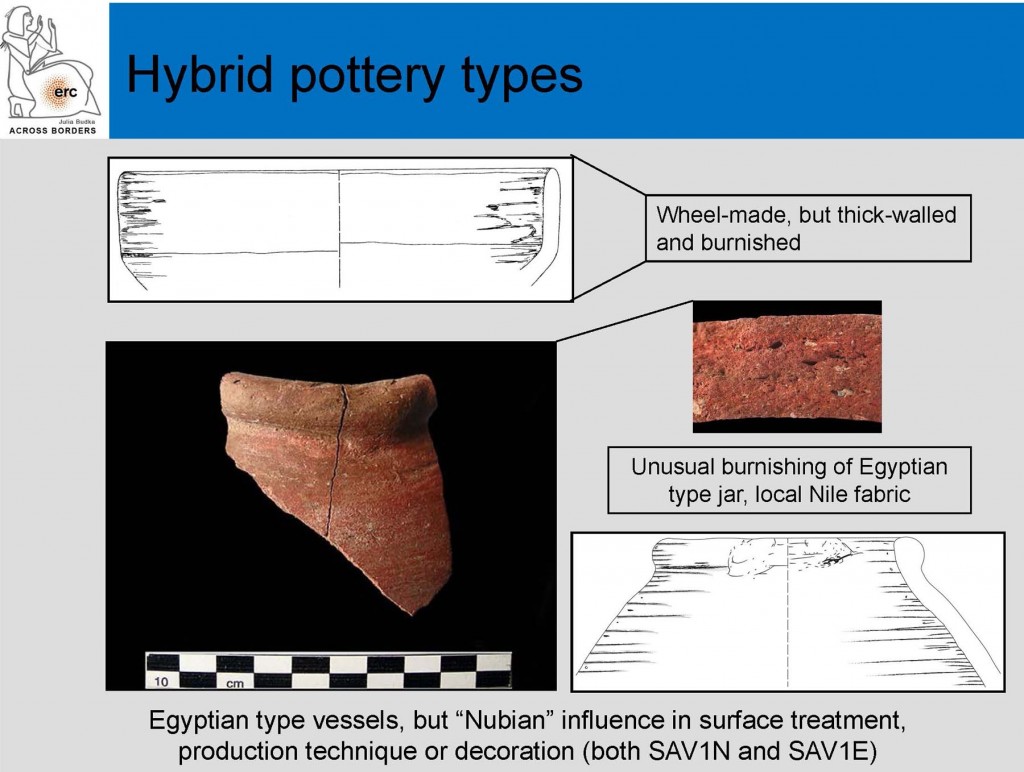
The prime feature which characterises the pottery vessels as feminoform vases are nipples or breasts applied to the upper part of the body of the jar. They are attested both as pierced ones, potentially functioning as small spouts, or as unpierced examples with a greater emphasis on anatomical details of the female breast. Feminine faces at the neck may complement these breast applications, but are sometimes missing. Applied arms including hands are present in some cases; sometimes they are executed in paint only.
At SAV1N, the excavation area in the north of the fortified New Kingdom town of Sai Island, two fragments of feminoform vases were found (see Budka forthc.). A surface find completes this small assemblage of three figure vases from 18th Dynasty Sai. The latter, a sherd collected by Francis Geus in 1998 from the surface, cannot be dated by context. It is a heavily worn shoulder fragment of a Marl A3 vessel. Modelled arms and hands are cupping the female breasts which are not pierced. There are no traces of wavy lines or incised comb patterns, as attested for an otherwise very similar jar from a tomb at Qustul (Bourriau 1982: 78, no. 50, Chicago 21044 from Qustul, tomb R. 29, early 18th Dynasty).

Fragment of feminoform vessel from Sai.
Although similar Marl A3 vessels are already known in the Middle Kingdom and the Second Intermediate Period, the comparison from Qustul and the archaeological context from Sai itself suggest a dating of the Marl A3 feminoform vessel to the early 18th Dynasty. It is significant (if tiny) evidence towards reconstructing Pharaonic lifestyle on Sai during the New Kingdom – which includes references to the general theme of regeneration and fertility as well as traces of “private religion” (cf. Stevens 2006).
References
Bourriau 1982 = J. Bourriau, No. 50: Milk vase, in E. Brovarski/S.K. Doll/R.E. Freed (eds.), Egypt’s Golden Age: The Art of Living in the New Kingdom, exhibition catalogue, Museum of Fine Arts Boston, Boston, 78.
Bourriau 1987 = J. Bourriau, Pottery Figure Vases of the New Kingdom, in Cahiers de la ceramique égyptienne 1 (1987), 81-96.
Budka forthc. = J. Budka, Vessels of life: New evidence for creative aspects in material remains from domestic sites, in: B. Bader, C.M. Knoblauch, E.C. Köhler (eds.), Vienna 2 – Ancient Egyptian Ceramics in the 21st Century. Proceedings of the International Conference held at the University of Vienna 14th-18th of May, 2012, Orientalia Lovaniensia Analecta [Leuven 2013-2014, forthcoming].
Hope 1982 = C.A. Hope, No. 69: Decorated vase, in E. Brovarski/S.K. Doll/R.E. Freed (eds.), Egypt’s Golden Age: The Art of Living in the New Kingdom, exhibition catalogue, Museum of Fine Arts Boston, Boston, 86-87.
Lopez Grande/de Gregorio 2009 = M.J. Lopez Grande/E. de Gregorio, Cerámicas del Reino Nuevo con decoración pintada y plástica halladas en Dra Abu el-Naga (excavaciones del Proyecto Djehuty), in M. Polo/M. Ángel/C. Sevilla Cueva (eds), Actas III Congreso Ibérico de Egiptología / III Congresso Ibérico de Egiptologia. Trabajos de Egiptología (Papers on Ancient Egypt 5:2), Puerto de la Croz (Tenerife), 31-48.
Seiler 2006 = A. Seiler, „Erhebe dich, Vater! …, deine Milch dir, die in den Brüsten deiner Mutter Isis ist.“ Zu Form und Funktion einer Gruppe anthropomorpher Gefäße aus der Nekropole in Dra’ Abu el-Naga/Theben, in E. Czerny et al. (eds.), Timelines. Studies in honour of Manfred Bietak (Orientalia Lovaniensia Analecta 149/1), Leuven, 317-327.
Smith 2003 = S.T. Smith, Wretched Kush. Ethnic identities and boundaries in Egypt’s Nubian Empire, London and New York.
Stevens 2006 = A. Stevens, Private Religion at Amarna (British Archaeological Reports, International Series 1587), Oxford.
 The last two weeks have been full of travelling and meetings, not in Egypt as originally planned, but here in Europe – the excellent Table ronde at Lille, a brilliant Kirwan Memorial Lecture by Vivian Davies at London, meetings with team members and future collaborators here in Vienna, planning for the next field season at Sai Island and placing orders for various equipment. Tonight, I hope to head for Vienna Airport the very last time in September – going to Berlin and picking up equipment, materials and my SUV there. Back to Vienna by car early next week – insha’allah!
The last two weeks have been full of travelling and meetings, not in Egypt as originally planned, but here in Europe – the excellent Table ronde at Lille, a brilliant Kirwan Memorial Lecture by Vivian Davies at London, meetings with team members and future collaborators here in Vienna, planning for the next field season at Sai Island and placing orders for various equipment. Tonight, I hope to head for Vienna Airport the very last time in September – going to Berlin and picking up equipment, materials and my SUV there. Back to Vienna by car early next week – insha’allah!