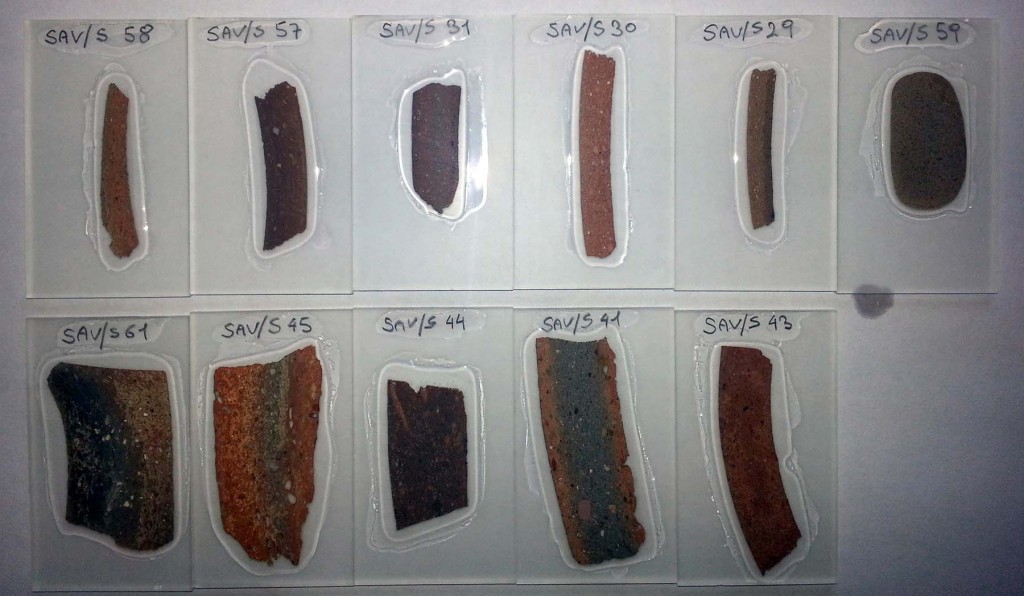
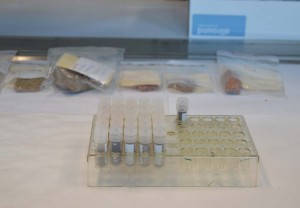
The scientific analyses of the first set of samples from the last Field Season (SIAM Mission 2013) are almost concluded in Vienna and the preliminary processing of the data has already shown some very interesting and intriguing results.
http://www.newbalanceshoesinc.com new balance running shoes
During the current season my main task is primarily selecting new ceramic specimens for the next analyses – having a large set of samples appears extremely important especially for the chemical results in order to improve the statistical reliability of the data! Beside many different New Kingdom wares (Egyptian and Local Nile clays, Nubian fabrics, Marl clays and Imports from Canaan, the Levant and the Oases) from the excavation areas SAV1 North, East and West within the Pharaonic town, we selected also some modern traditional ceramics to be used as comparative samples for the ancient production.
For this reason we went to the near-by city of Abri last week: Huda, our inspector of NCAM, and also Erich joined me – as a geologist Erich is also interested in seeing where the modern potters collect the raw material for their vessels.
http://www.airmaxfreedom.com kids air max 95
Not so far away from the centre of the village and from the area of the market there is in fact an intact ceramic workshop where a family of modern potters (‘bagadra’) still produce different kind of vessels according to a traditional recipe handed down from one generation to another!
Thanks to Huda (for this occasion our personal interpreter!) we had the unique opportunity to interview the potters and to ask them about their job, the function of the vessels and the manufacturing process!
http://www.airmaxfreedom.com air max griffey
The pots are wheel-made (on a slow wheel), even though the upper part of the vessel is sometimes finished by coiling. Before the firing, they are put for 2-3 days upside down in the sand and then left some more days under the sun till they become completely dry.
Over 50 vessels are produced and then sold to Abri, Sai, Ernetta and even to Khartoum every month! This production consists mainly in large jars (zir) used for containing and keeping cool water, but they also make smaller vessels (e. g. milk/mish jars), cooking pots (hala), flower pots, incense burners and so on!
http://www.nikefreerunshoesplus.com nike free reviews
In addition, what appears really interesting is that the potters seem partially to differentiate their ‘recipe’ (in terms of choice of clayey raw material and tempers), according to the specific function and the performance required by the vessel!
We learnt a lot from this conversation and we came back home very inspired bringing with us some nice ceramic pieces kindly offered by the potters – they have been already documented and will be soon submitted for the next laboratory analyses!